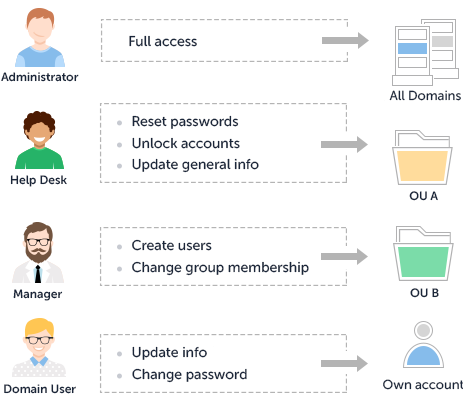
Active Directory management involves many different operations that require administrative privileges granted by default to AD administrators only. Though operations like password reset or account unlock are pretty simple, they take a lot of time of highly-skilled IT staff, not allowing them to focus on more complex and important issues. Active Directory delegation helps you optimise the productivity of the IT department by letting non-administrative users (e.g. department managers or Help Desk operators) perform certain administrative activities in Active Directory.
Active Directory delegation helps you significantly enhance the security of the environment, decentralise Active Directory administration, and successfully address the administrative needs of the organisation, making Active Directory management more efficient and cost-effective.
Native Active Directory Delegation
The native Active Directory delegation model has a number of disadvantages that prevent you from taking a granular approach to the delegation of rights in Active Directory. Since there is no central place to store permissions, Active Directory delegation introduces a rather tedious and error-prone manual maintenance of multiple ACLs across Active Directory and makes it rather challenging to control what permissions and privileges are granted to users. This lack of control often results in many users having administrative access that is not necessary for performing their job functions, thus creating various security threats and causing audit failures.
Another major disadvantage of the native Active Directory delegation model is the lack of the ability to grant user access based on the job function. To provide the permissions necessary to perform a certain job role, administrators have to manually assign multiple sets of various rights across a large set of objects in Active Directory. It is even more difficult to revoke all unnecessary privileges from the users whose responsibilities or the role in the organisation have changed. Such an approach allows much room for errors and omissions that often result in users either not having the permissions they need, or having elevated administrative privileges they don't need.
Role-Based Approach to Active Directory Delegation
Adaxes brings Active Directory delegation to a higher level by introducing the particularly effective and proven role-based access control model. Role-based administration allows you to delegate responsibilities based on business functions and administrative scopes in a centralised manner. Using administrative security roles you can easily delegate multiple permissions to and subsequently revoke delegated privileges from multiple users performing the same job function without modification of native Active Directory permissions. As access rights are managed centrally, you can efficiently control who has what permissions on what resources in Active Directory.
All permissions necessary to perform a certain job function are aggregated into Security Roles that are assigned to users in accordance with their job role in the organisation. For example, administrative duties related to user account support (e.g. password reset, unlock accounts, rename users) are usually assigned to a specific set of technicians for a specific collection of user accounts. By defining a Security Role called Help Desk, you can associate with that role a set of permissions necessary to provide account support. You can then assign this role to various users and groups over different scopes of influence within the organisation. To grant or revoke privileges for all users performing the Help Desk role, you simply need to modify the set of permissions assigned to that role.
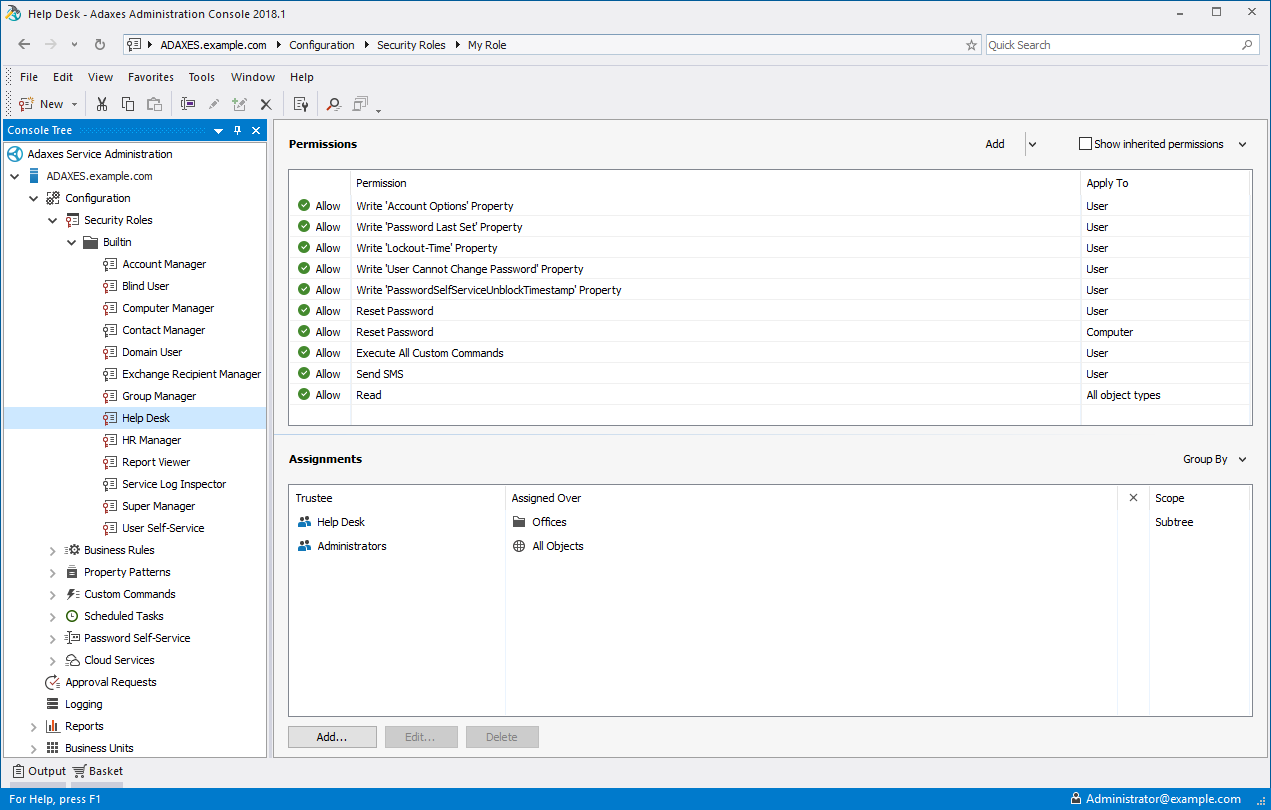
Scope of Active Directory Delegation
One of the well-known limitations of the native Active Directory delegation model is that it allows you to delegate permissions with a scope limited to either entire AD domain or a specific Organisational Unit. But what if you need to allow your Help Desk staff to perform the delegated activities on all members of the Sales department that are spread across multiple OUs or AD domains? Or what to do if members of all departments are located in one and the same OU, but you want to delegate permissions on the members of the Sales department only?
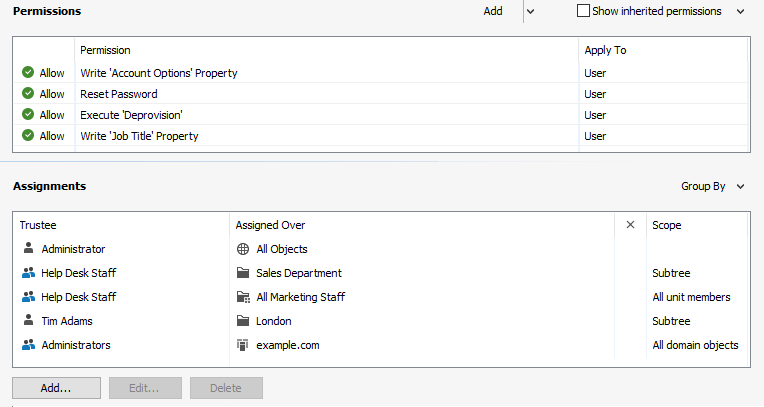
Adaxes facilitates Active Directory delegation by enabling a more granular and accurate assignment of rights by allowing you to delegate permissions over all objects in one or several AD domains, objects located under specific OUs, members of AD groups, specific AD objects, and members of virtual OUs called Business Units.
Using Business Units for the distribution of administrative rights significantly facilitates Active Directory delegation, as Business Units can include Active Directory objects located in different OUs, AD domains and even forests. For example, you may need to delegate administrative rights to Help Desk technicians on all users from the Sales department that are spread across multiple AD locations. For this purpose, you can define a Business Unit that includes all users whose Department property is set to 'Sales', and assign the Help Desk role to a group of technicians over the members of that Business Unit.
Moreover, the scope where users can apply their permissions can include the objects managed by them or their direct reports. For example, if you want to allow managers to manage the accounts of their direct reports, you need to assign a Security Role to Manager. Or, if you want to delegate certain permissions for an AD object to the user who manages the object, you need to grant the permissions to Owner (Managed By). Once a manager changes, the permissions will be revoked and granted to the new manager automatically, which saves you the effort of reassigning permissions manually.
Active Directory Delegation with Approvals
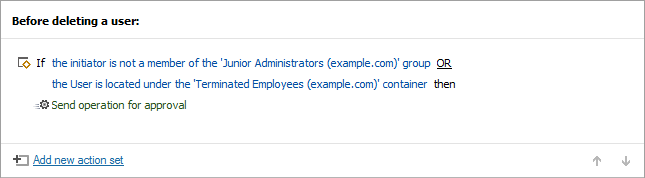
Adaxes makes Active Directory delegation even more secure and compliant, as it allows you to control how the delegated activities are carried out. Adaxes can be configured to perform certain operations in Active Directory only after an approval is given by an authorised person. It is also possible to specify conditions that must be met for an operation to require an approval. For example, an approval for user deletion can be requested only if the operation is performed by a member of the Junior Administrators group, or the user account is not located under the Terminated Employees organisational unit.
The role-based security model provided by Softerra Adaxes significantly facilitates Active Directory delegation as it enables granular assignment of administrative permissions based on job roles, eliminating the need to manually modify multiple ACLs across Active Directory. As all permissions are stored in a central location, you can easily track and monitor the delegated rights across AD domains. Flexible assignment of security roles helps you ensure that all users have the least privileges necessary to perform their job function.
Other Features
Active Directory Management
Adaxes features a rule-based platform for Active Directory, Exchange and Office 365 automation, provides an enhanced web-based management environment, gives you a role-based access control model for delegating privileges, adds security with approval-based workflow, allows enforcing corporate data standards and much more.
More InfoActive Directory Automation
Adaxes provides rule-based automation for Active Directory, Exchange and Office 365. It allows executing sets of operations that are governed by if/else conditions before or after certain events in AD. So, for example, after the department of a user is changed, Adaxes can then automatically update the user’s group membership and send an email notification to the user’s manager, following the rules you define.
More InfoActive Directory Provisioning
Using condition-based rules you can automate the entire user provisioning process. Once a new user account is created in Active Directory, Adaxes will automatically execute the rest of onboarding procedures for you: moving the user account to a correct OU, adding it to necessary groups, creating and configuring an Exchange mailbox, assigning Office 365 licences, enabling the user for Skype for Business, creating and sharing a home folder, sending a welcome email, etc. Similarly to that, you can also automate all operations associated with user updates. Finally, when a user is terminated, Adaxes can automatically execute all the provisioning operations in reverse, ensuring instant and errorless offboarding.
More InfoWeb Interface for Active Directory
Adaxes Web Interface enables Active Directory management via a standard web browser. It features a modern responsive design, so users can access it on their laptops, tablets, phones or any other devices. You can set up different Web Interfaces specifically tuned for the needs of different job roles, like administrators, help desk, HR, managers, and others, giving them a clean and intuitive way to access the tasks they need. Adaxes Web Interface also incorporates Exchange and Office 365 management, so users get a single console without the need to learn and use multiple tools for their day-to-day routines.
More InfoWeb Interface Customisation
The Adaxes Web Interface is fully customisable, so you can configure it to have the exact views, forms, and operations that each user needs. For example, administrators can have a full set of management activities in Active Directory, Exchange and Office 365 across the entire environment, whereas managers can be set to view just their subordinates and only be able to update their group membership, assign Office 365 licences and change certain AD properties.
More InfoActive Directory Self Service
Adaxes Web Interface can act as a self-service portal for regular users. You can granularly specify, which operations they have access to, like updating their personal info, changing their own password, searching Active Directory, managing own group membership, updating Office 365 licences, etc.
More InfoActive Directory Password Self-Service
Adaxes Password Self-Service allows users to reset forgotten passwords and unlock accounts by themselves. To do that they need to go through a simple identity verification procedure that may involve answering security questions, SMS verification, using authenticator apps like Google Authenticator, Authy and others. A self-password reset can be accessed from the Windows logon screen, Adaxes Web Interface or it can be integrated into your own portal.
More InfoExchange Management and Automation
Adaxes automates Exchange mailbox management both on-premises and in Office 365. For example, after creating a new user account in Active Directory, Adaxes can automatically create an Exchange mailbox for the user. The database distribution of mailboxes can be done based on the first letter of the users’ surname, least number of mailboxes in the DB, the round-robin method, etc. Adaxes can then configure the mailbox, e.g. modify storage quotas or enable mailbox features like Unified Messaging or Archiving.
More InfoOffice 365 Automation and management
Adaxes can automatically assign and revoke Office 365 licences using condition-based rules. For example, when a new user is created in Active Directory, Adaxes can activate an account in Office 365 for the user and assign the necessary O365 licences according to the rules you define. Different licences can be assigned to different users based on their job title, department, location, etc.
More InfoActive Directory Role-Based Security
Adaxes introduces Role-Based Access Control for Active Directory, Exchange and Office 365. In a role-based delegation model, instead of assigning permissions to users, they are assigned to roles that correspond to actual job functions. So, when you need to change privileges for all users with the same job function, all you need to do is modify the permissions of the associated role. Assigning roles to users is done in a centralised manner, allowing you to easily control, who can do what and where. With role-based delegation, you can granularly specify, which parts of Active Directory are visible to users. For example, you can allow certain users to only view AD objects located in their own OU, while hiding the rest of the Active Directory structure from them.
More InfoApproval-Based Workflow
Adaxes allows you to add an approval step to practically any operation in Active Directory, Exchange and Office 365. For example, you can delegate user creation to HR, but after they fill in the form and click Create, Adaxes can suspend the operation and only proceed once a member of IT staff reviews and approves it. For more complex and security-sensitive scenarios, you can set up multi-level approvals. Such an approach allows delegating more tasks to lower level staff without taking the risk of losing control over them.
More InfoActive Directory Reports
Adaxes comes with reporting capabilities, allowing you to monitor and analyse what’s going on in your environment. Out of the box, you get more than 200 reports, which should cover the majority of your requirements. For more demanding scenarios Adaxes also provides various ways to create custom reports, including using your own scripts. It enables you to create reports of practically any complexity that can be specific to your organisation's needs. To deliver reports to users Adaxes supports centralised scheduling and also provides a self-scheduling option, allowing users to choose by themselves, which reports they want to receive and when.
More InfoCustom Commands for Active Directory
With Custom Commands users can launch complex multi-step operations in one go. For example, if you need to send a user on vacation, you can do it with just one click in the Web Interface. The operation can include steps like disabling the user account, adding it to a corresponding group, sending a notification to the user’s manager, etc. Such an approach allows you to delegate complicated tasks to users and not worry that they will miss a step or do something wrong. Besides, you don’t over-privilege them, as you only give out permissions to execute the Custom Command as a whole, not the individual steps it consists of. Administrators can also use Custom Commands in their day-to-day routines to make the management process simpler and accomplish the same results with a lot fewer clicks.
More InfoScheduled Tasks for Active Directory Management
Adaxes allows you to automate various routine management tasks by scheduling them. For example, it can automatically de-provision inactive accounts in AD, allocate users to necessary groups, maintain OU structure, etc. You can also schedule tasks like importing new users from CSV. Automating such a sensitive operation doesn’t mean that you need to sacrifice any control, as you can add an approval step to it. This way users will be created in AD only after a member of IT staff reviews and approves the operation. You can also use scheduled tasks to send various notifications to users, like reminders about their password or account expiration.
More InfoActive Directory Delegation
Active Directory management involves many different operations that require administrative privileges granted by default to AD administrators only. Though operations like password reset or account unlock are pretty simple, they take a lot of time of highly-skilled IT staff, not allowing them to focus on more complex and important issues. Active Directory delegation helps you optimise the productivity of the IT department by letting non-administrative users (e.g. department managers or Help Desk operators) perform certain administrative activities in Active Directory.
More Info

